May 10, 2021
Development of a New Synthetic Method to Synthesize Quinazolinone Derivatives
Reducing Environmental Impact and Accelerating Drug Development

The results of this research were published in the journal “Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis” on June 23, 2021.
Key points
- The researchers succeeded in developing a new method for the efficient synthesis of biologically active quinazolinone derivatives under environmentally friendly conditions using the “multicomponent coupling reaction”, in which three components (isatoic anhydride, benzyl alcohol, and amine) reacted in a single flask.
- In this method, benzyl alcohol can be used, as it uses water as the solvent and a water-soluble palladium catalyst.
- This method does not require toxic oxidants or organic solvents and is an environmentally friendly and efficient for constructing heteroaromatic rings that reduces the number of reaction steps and waste, and accelerates drug development.
Summary
In multicomponent coupling reaction, three or more components react in a single flask to produce a single product and is often used in drug discovery research. For example, a biologically active quinazolinone derivative can be synthesized by adding an oxidant to three components (isatoic anhydride, benzaldehyde, and amine) in an organic solvent. However, since it requires a large amount of highly toxic oxidants and the preparation of benzaldehyde from alcohol, the development of a catalytic synthesis method with less environmental impact is warranted.
The group has succeeded in developing a new environmentally-friendly, multi-component coupling reaction for the synthesis of quinazolinones using water as a solvent and a water-soluble palladium catalyst. By adding a palladium catalyst to the above-mentioned three components using water as the solvent, benzyl alcohol, which has low reactivity, can be used directly in the multicomponent coupling reaction, enabling more efficient synthesis of quinazolinone derivatives.
In multicomponent coupling reaction, three or more components react in a single flask to produce a single product and is often used in drug discovery research. For example, a biologically active quinazolinone derivative can be synthesized by adding an oxidant to three components (isatoic anhydride, benzaldehyde, and amine) in an organic solvent. However, since it requires a large amount of highly toxic oxidants and the preparation of benzaldehyde from alcohol, the development of a catalytic synthesis method with less environmental impact is warranted.
The group has succeeded in developing a new environmentally-friendly, multi-component coupling reaction for the synthesis of quinazolinones using water as a solvent and a water-soluble palladium catalyst. By adding a palladium catalyst to the above-mentioned three components using water as the solvent, benzyl alcohol, which has low reactivity, can be used directly in the multicomponent coupling reaction, enabling more efficient synthesis of quinazolinone derivatives.
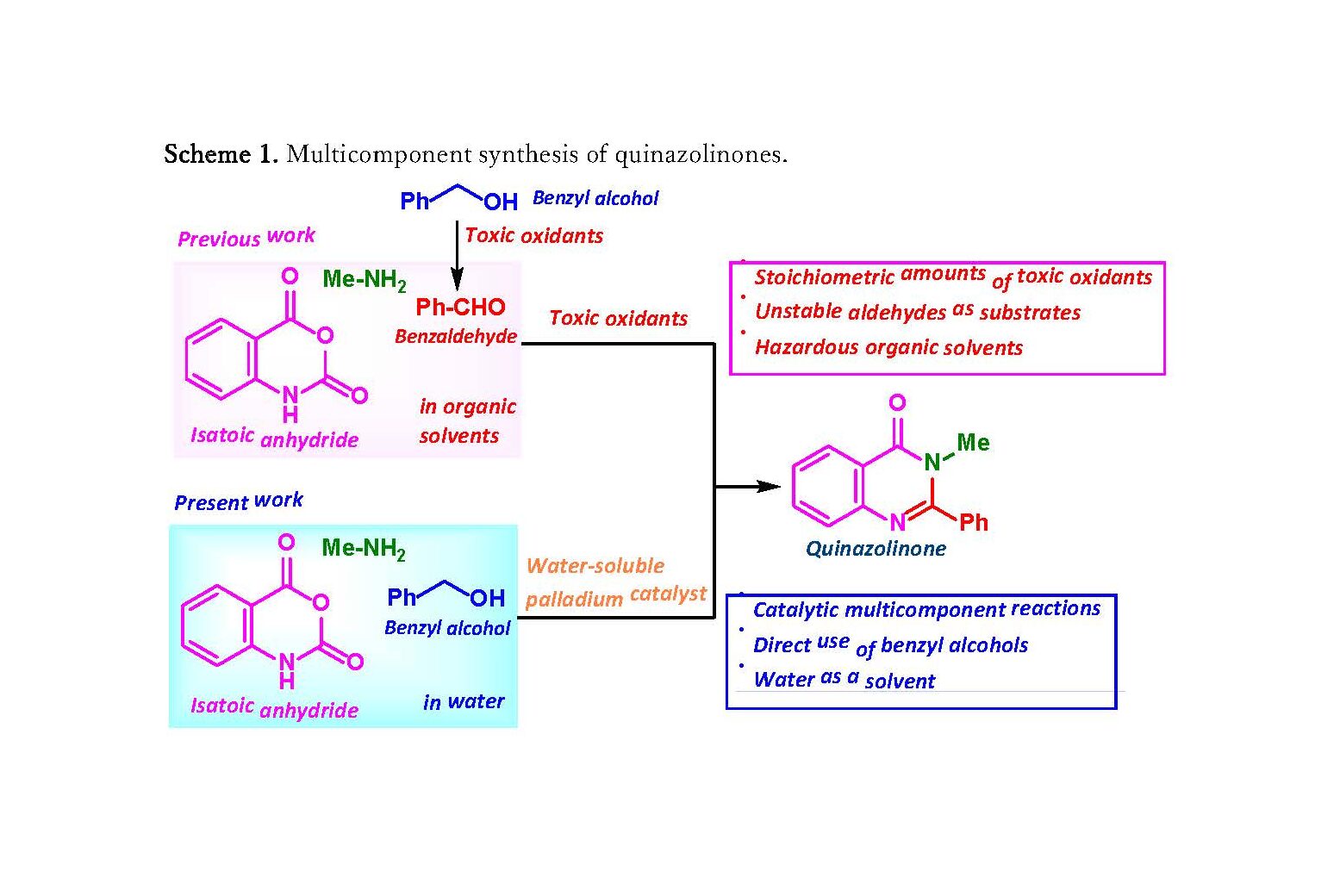
Scheme 1
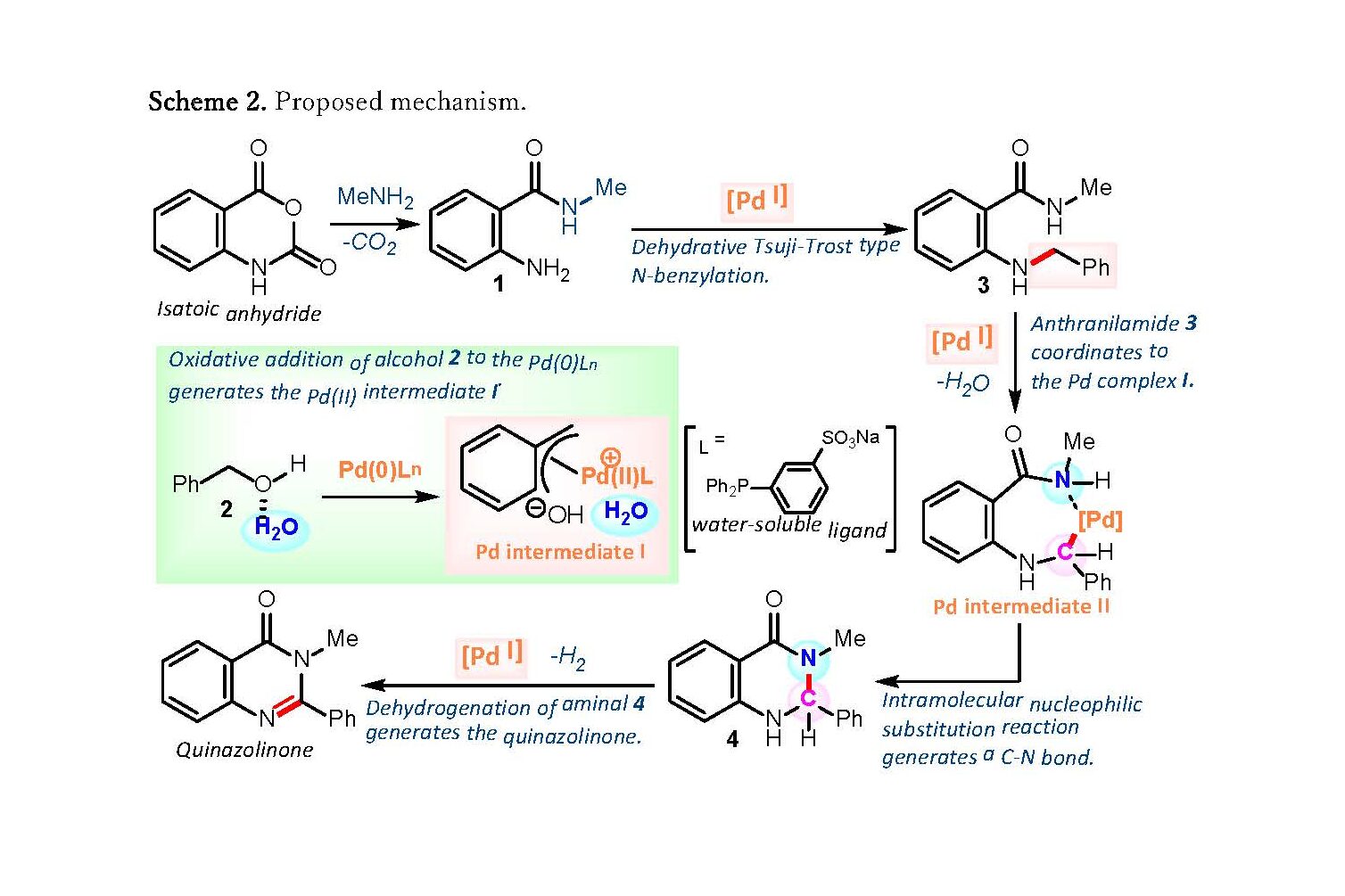
Scheme 2
Journal name
Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis (June 23, 2021)
Title of paper
Direct Use of Benzylic Alcohols for Multicomponent Synthesis of 2-Aryl Quinazolinones Utilizing the π-Benzylpalladium(II) System in Water
Author(s)
Hidemasa Hikawa*, Taku Nakayama, Makiko Takahashi, Shoko Kikkawa and Isao Azumaya* (*Responsible Author)
DOI No.
org/10.1002/adsc.202100535.
Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis (June 23, 2021)
Title of paper
Direct Use of Benzylic Alcohols for Multicomponent Synthesis of 2-Aryl Quinazolinones Utilizing the π-Benzylpalladium(II) System in Water
Author(s)
Hidemasa Hikawa*, Taku Nakayama, Makiko Takahashi, Shoko Kikkawa and Isao Azumaya* (*Responsible Author)
DOI No.
org/10.1002/adsc.202100535.
READ MORE RESEARCH NEWS - Pharmaceutical Sciences
ACADEMICS
Undergraduate Programs
– Medicine
– Pharmaceutical Sciences
– Science
– Nursing
– Health Science
Graduate Programs
–Medicine
–Pharmaceutical Sciences
–Science
–Nursing
Undergraduate Programs
– Medicine
– Pharmaceutical Sciences
– Science
– Nursing
– Health Science
Graduate Programs
–Medicine
–Pharmaceutical Sciences
–Science
–Nursing
RESEARCH
– News
– Guidelines & Policies
– Support Offices
– Facilities
– Security Export Control
Non-Degree Programs
– Clinical Elective Program
– International Physician Observership Program

.jpg)
