August 19, 2021
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Immediately Inhibits the Contractile Response of Coronary and Basilar Arteries through Inhibiting Prostanoid TP Receptors


Key points
- DHA exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, and its long-term intake reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular disease. However, little research has been done on the immediate effects of DHA in functional vessels such as coronary arteries and cerebral arteries, which are frequent sites of spasm and target sites for therapeutic agents such as Ca2+ antagonists.
- In this study, we found that DHA selectively and potently inhibited the contractile responses mediated by the prostanoid TP receptor in porcine coronary arteries and basilar arteries. DHA selectively inhibited the prostanoid TP receptor-mediated cellular response in cells expressing human prostanoid TP receptors
- The results indicated that the prostanoid TP receptor may be associated with abnormal constriction of coronary arteries and cerebral arteries. These findings suggest that DHA may prevent the abnormal contraction of coronary arteries and cerebral arteries triggered by thromboxane A2 and contractile prostaglandins, thereby reducing the incidence of cardiovascular diseases caused by these contractions.
Summary
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid that is abundantly present in fish oil. It is a relatively well-known ingredient of health foods and supplements. Long-term intake of DHA has a preventive effect against hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases. This effect is generally attributed to the inhibition of the production of inflammatory substances such as prostanoids. However, the immediate effects of DHA on vascular tone have not been thoroughly investigated. The research group led by Dr. Kento Yoshioka, Dr. Keisuke Obara and Professor Yoshio Tanaka found that DHA selectively and strongly inhibited the contractile responses to prostanoids in coronary and basilar arteries, which are the most common sites for cardiovascular diseases such as angina pectoris and cerebral vasospasm. The results of this study showed that DHA intake might have a strong preventive effect against the cardiovascular diseases caused by abnormal contraction of coronary arteries and basilar arteries, revealing, for the first time, that part of the cardiovascular protective effect of DHA may be related to its inhibitory effect on prostanoid TP receptors.
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid that is abundantly present in fish oil. It is a relatively well-known ingredient of health foods and supplements. Long-term intake of DHA has a preventive effect against hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases. This effect is generally attributed to the inhibition of the production of inflammatory substances such as prostanoids. However, the immediate effects of DHA on vascular tone have not been thoroughly investigated. The research group led by Dr. Kento Yoshioka, Dr. Keisuke Obara and Professor Yoshio Tanaka found that DHA selectively and strongly inhibited the contractile responses to prostanoids in coronary and basilar arteries, which are the most common sites for cardiovascular diseases such as angina pectoris and cerebral vasospasm. The results of this study showed that DHA intake might have a strong preventive effect against the cardiovascular diseases caused by abnormal contraction of coronary arteries and basilar arteries, revealing, for the first time, that part of the cardiovascular protective effect of DHA may be related to its inhibitory effect on prostanoid TP receptors.
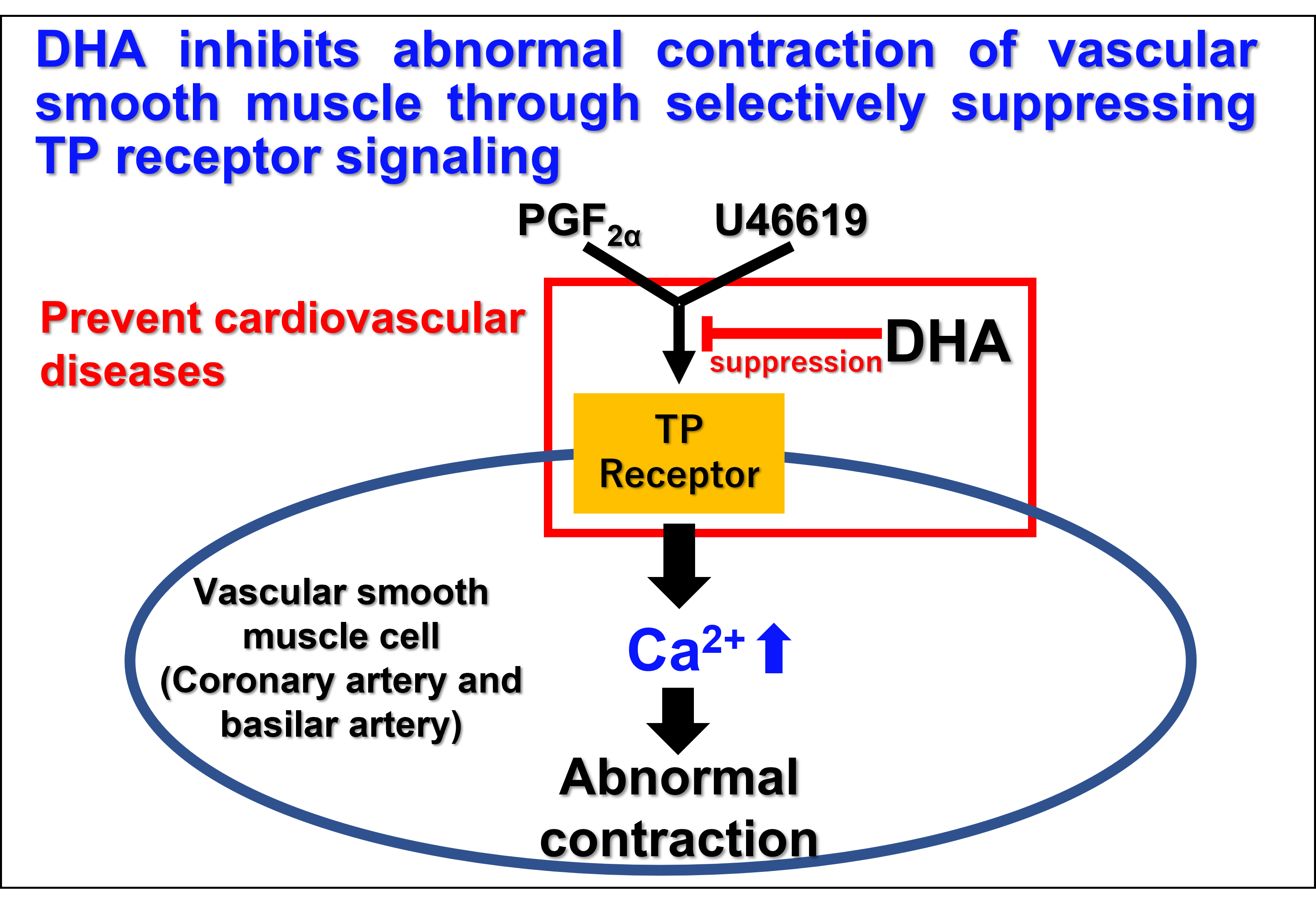
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the research results
Authors:
Kento Yoshioka (Assistant Professor, Department of Chemical Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Toho University)
Keisuke Obara (Lecturer, Department of Chemical Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Toho University)
Yoshio Tanaka (Professor, Department of Chemical Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Toho University)
Kento Yoshioka (Assistant Professor, Department of Chemical Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Toho University)
Keisuke Obara (Lecturer, Department of Chemical Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Toho University)
Yoshio Tanaka (Professor, Department of Chemical Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Toho University)
READ MORE RESEARCH NEWS - Pharmaceutical Sciences
ACADEMICS
Undergraduate Programs
– Medicine
– Pharmaceutical Sciences
– Science
– Nursing
– Health Science
Graduate Programs
–Medicine
–Pharmaceutical Sciences
–Science
–Nursing
Undergraduate Programs
– Medicine
– Pharmaceutical Sciences
– Science
– Nursing
– Health Science
Graduate Programs
–Medicine
–Pharmaceutical Sciences
–Science
–Nursing
RESEARCH
– News
– Guidelines & Policies
– Support Offices
– Facilities
– Security Export Control
Non-Degree Programs
– Clinical Elective Program
– International Physician Observership Program

.jpg)
