Novel role of microRNA 146b-5p for repression of scar formation in skin wounds

Prof. Akasaka (front row, second from right) and members of the Department of Pathology
- miR-146b-5p suppress fibrosis and scar formation via its targeting repression of PDGFRα expression in rat skin wounds.
- Inhibited PDGFRα expression in adipose stromal cells by miRNA146b-5p was shown as a new mechanism for suppression of scar formation in skin wounds.
- Identifying the role of miR-146b-5p in inhibited scar formation will not only reveal the mechanism of scar formation in skin wounds but also to develop a therapeutic strategy to prevent dysfunction resulting from fibrosis in injured organs, possibly due to inhibiting fibrosis via miR-146b-5p administration.
The findings from this study will not only elucidate the mechanism of adipose tissue-mediated scar fibrosis in skin wounds, but also may prevent dysfunction caused by organ fibrosis by suppressing scar fibrosis in damaged organs via miRNA146b-5p administration.
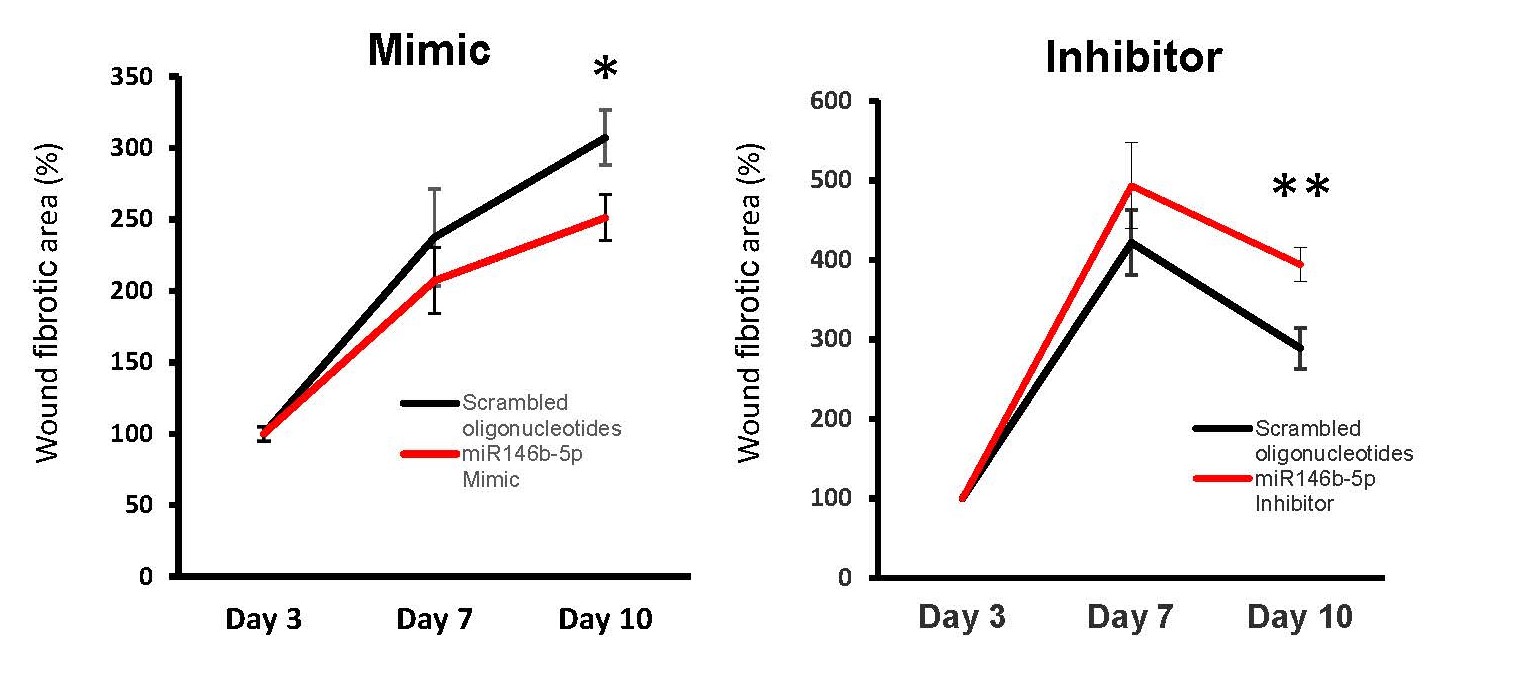
Figure 1. Attenuation of dermal fibrosis by miRNA146b-5p in skin wounds. The proportion of fibrotic area in miRNA146b-5p mimic-treated wounds was significantly smaller than that in scrambled RNA-treated wounds. In contrast, the proportion of fibrotic area at day 10 in miRNA146b-5p inhibitor-treated wounds was significantly larger than that in scrambled RNA-treated wounds. Y. Akasaka et al. The role for miRNA146b-5p in the attenuation of dermal fibrosis and angiogenesis by targeting PDGFRα in skin wounds. Reprinted with permission from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2021.11.037.
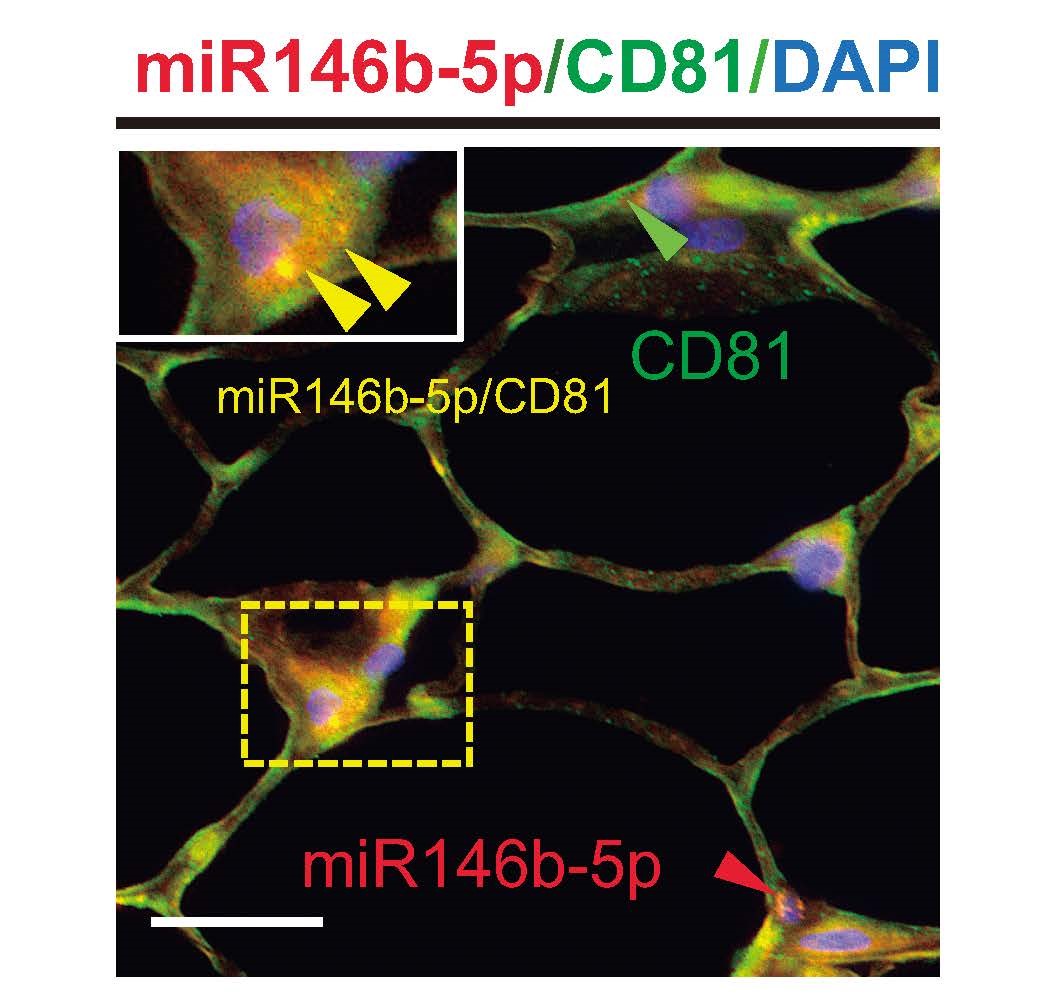
Figure 2. Wound adipose tissue cells exhibit CD81 exosomes containing miRNA146b-5p. Combined staining with miRNA146b-5p (red) and CD81 (green) highlights double-positive granules for CD81 and miRNA146b-5p (yellow) in the adipose tissue cells of mimic-transfected wounds. Y. Akasaka et al. The role for miRNA146b-5p in the attenuation of dermal fibrosis and angiogenesis by targeting PDGFRα in skin wounds. Reprinted with permission from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2021.11.037.
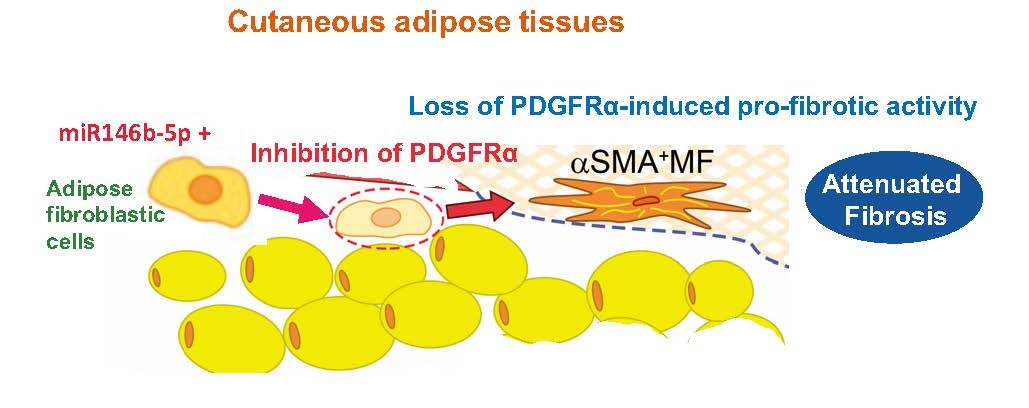
Figure 3. miRNA146b-5p-targeted repression of PDGFRα in adipose tissue cells can lead to a loss of their PDGFRα-induced profibrotic activities, resulting in reduction in skin wound fibrosis. MF, myofibroblast; SMA, smooth muscle actin. Y. Akasaka et al. The role for miRNA146b-5p in the attenuation of dermal fibrosis and angiogenesis by targeting PDGFRα in skin wounds. Reprinted with permission from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2021.11.037.
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (Published on-line: December 18, 2021)
Title:
The role for miRNA146b-5p in the attenuation of dermal fibrosis and angiogenesis by targeting PDGFRα in skin wounds
Authors:
Chie Fujisawa, Makoto Hamanoue, Yayoi Kawano, Daiki Murata, Yuri Akishima-Fukasawa, Tetsuya Okaneya, Takeo Minematsu, Hiromi Sanada, Kayo Tsuburaya, Takuma Isshiki, Tetuo Mikami, Takehisa Hanawa, Yoshikiyo Akasaka* (*Responsible author)
DOI No.
10.1016/j.jid.2021.11.037
READ MORE RESEARCH NEWS - MEDICINE
Undergraduate Programs
– Medicine
– Pharmaceutical Sciences
– Science
– Nursing
– Health Science
Graduate Programs
–Medicine
–Pharmaceutical Sciences
–Science
–Nursing
RESEARCH
– News
– Guidelines & Policies
– Support Offices
– Facilities
– Security Export Control
Non-Degree Programs
– Clinical Elective Program
– International Physician Observership Program