July 7, 2022
DHA Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Death in Schwann Cells
Suggesting a new preventive effect of DHA on diabetic neuropathy by regulating autophagy


A research group comprising Dr. Yasuaki Tatsumi of Toho University Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences and members of Aichi Gakuin University School of Pharmacy have demonstrated that docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) reduces cell death by regulating autophagy induced by oxidative stress in rat Schwann cells. Further research is expected to reveal new preventive effects of DHA on the onset and progression of diabetic neuropathy. The results were published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences on April 15, 2022.
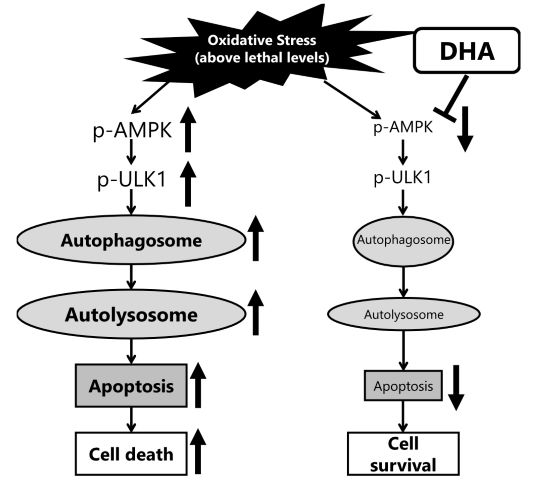
Figure 1. Schematic diagram illustrating the effect of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on autophagosomes in response to lethal levels of oxidative stress.
Key points
- The research group previously reported that DHA induces antioxidant enzymes and protects Schwann cells from oxidative stress. However, the effect of DHA on autophagy, which is closely related to oxidative stress, was not clarified.
- In this study, researchers revealed part of the mechanism by which pre-administration of DHA suppresses autophagy induced by oxidative stress, thereby reducing cell death.
- The results of the study suggest that DHA may have a preventive effect on the onset and progression of diabetic neuropathy by regulating autophagy, while also inducing antioxidant enzymes as reported previously.
Summary
Dr. Yasuaki Tatsumi of Toho University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Prof. Koichi Kato of Aichi Gakuin University School of Pharmacy and their research group had previously reported that docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) induces antioxidant enzymes and protects Schwann cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death.
However, the relationship between autophagy and oxidative stress-induced cell death, thought to be closely related to oxidative stress — one of the major causes of diabetic neuropathy, remained unclear.
In this study, they investigated the relationship between DHA and autophagy on oxidative stress-induced cell death using rat immortalized Schwann cell line. The results showed that pre-administration of DHA suppressed oxidative stress-induced cell death, and as a mechanism, suppressed autophagy signaling induced by oxidative stress. This suggests that DHA may inhibit cell death of Schwann cells by regulating autophagy induced by oxidative stress, in addition to the induction of antioxidant enzymes as reported previously.
Dr. Yasuaki Tatsumi of Toho University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Prof. Koichi Kato of Aichi Gakuin University School of Pharmacy and their research group had previously reported that docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) induces antioxidant enzymes and protects Schwann cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death.
However, the relationship between autophagy and oxidative stress-induced cell death, thought to be closely related to oxidative stress — one of the major causes of diabetic neuropathy, remained unclear.
In this study, they investigated the relationship between DHA and autophagy on oxidative stress-induced cell death using rat immortalized Schwann cell line. The results showed that pre-administration of DHA suppressed oxidative stress-induced cell death, and as a mechanism, suppressed autophagy signaling induced by oxidative stress. This suggests that DHA may inhibit cell death of Schwann cells by regulating autophagy induced by oxidative stress, in addition to the induction of antioxidant enzymes as reported previously.
Journal:
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, April 15, 2022 issue, Volume 23 No.8, 4405
Title:
Docosahexaenoic Acid Suppresses Oxidative Stress-Induced Autophagy and Cell Death via the AMPK-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Immortalized Fischer Rat Schwann Cells 1
Authors:
Yasuaki Tatsumi, Ayako Kato, Naoko Niimi, Hideji Yako, Tatsuhito Himeno, Masaki Kondo, Shin Tsunekawa, Yoshiro Kato, Hideki Kamiya, Jiro Nakamura, Koji Higai, Kazunori Sango, Koichi Kato
DOI No.
10.3390/ijms23084405
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, April 15, 2022 issue, Volume 23 No.8, 4405
Title:
Docosahexaenoic Acid Suppresses Oxidative Stress-Induced Autophagy and Cell Death via the AMPK-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Immortalized Fischer Rat Schwann Cells 1
Authors:
Yasuaki Tatsumi, Ayako Kato, Naoko Niimi, Hideji Yako, Tatsuhito Himeno, Masaki Kondo, Shin Tsunekawa, Yoshiro Kato, Hideki Kamiya, Jiro Nakamura, Koji Higai, Kazunori Sango, Koichi Kato
DOI No.
10.3390/ijms23084405
READ MORE RESEARCH NEWS - Pharmaceutical Sciences
ACADEMICS
Undergraduate Programs
– Medicine
– Pharmaceutical Sciences
– Science
– Nursing
– Health Science
Graduate Programs
–Medicine
–Pharmaceutical Sciences
–Science
–Nursing
Undergraduate Programs
– Medicine
– Pharmaceutical Sciences
– Science
– Nursing
– Health Science
Graduate Programs
–Medicine
–Pharmaceutical Sciences
–Science
–Nursing
RESEARCH
– News
– Guidelines & Policies
– Support Offices
– Facilities
– Security Export Control
Non-Degree Programs
– Clinical Elective Program
– International Physician Observership Program

.jpg)
